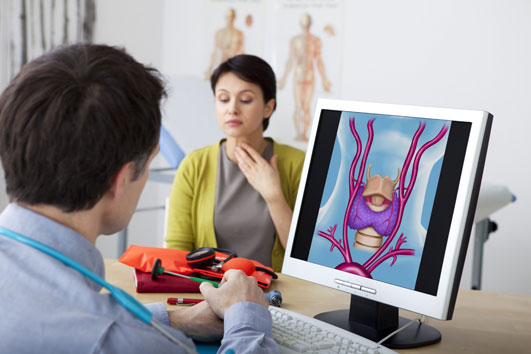
What is?
The thyroid is a very important gland, located in the area of our throat, over the trachea and directly under the larynx. The thyroid manages important functions of the human body. It regulates the combustions in cells, growth, metabolism, as well as our mental health and balance. The biological actions of the thyroid gland are performed through the produced Τ3 and Τ4 hormones, for the composition of which, the presence of iodine is required.
Thyroid gland problems
Hyperthyroidism
It is the condition where the thyroid gland secretes higher quantities of thyroid hormones than normal
In the case of hyperthyroidism the patients may show increased nervousness, tremor of the extremities, insomnias, tachycardia, shortness of breath and frequent fatigue. Furthermore, they may feel hot, may present increased appetite and, while they eat much, they may lose weight. Patients with hyperthyroidism may present exophthalmos (bulging of the eyes).
In more detail: Hyperthyroidism
- Tachycardia
- Nervousness
- Decreased endurance
- Diarrhea
- Hyperhidrosis (excessive sweating)
- Muscular weakness
- Tremor in the arms
- Weight loss, despite the good appetite
- Heat intolerance
- Hair loss
- Skin problems
- Menstrual disorders
- Exophthalmos
- Goiter
The thyroid gland is enlarged and there is a swelling in the throat area.
Hypothyroidism
It is the condition where the thyroid secretes decreased quantities of hormones.
The patient may present intense fatigue, physical weakness and drowsiness, even slow speech rate. Furthermore, there may be sensitivity to cold, dry skin or weight increase.
In more detail: Hypothyroidism
- Weakness
- Decreased endurance
- Constipation
- Arthritis
- Xerodermia (Dry skin)
- Memory disorders
- Menstrual disorders
- Fertility disorders
- Cramps
- Depression
- Somnolence
- Increase of body weight
Treatment
The thyroid disorders are generally treated with medication and systematic examinations by the endocrinologist. If, despite the medication, the results of the treatment are insufficient, the surgical treatment is recommended, which is the only solution in the case where the thyroid gland must be removed – thyroidectomy (for example, thyroid cancer).
Thyroid nodules
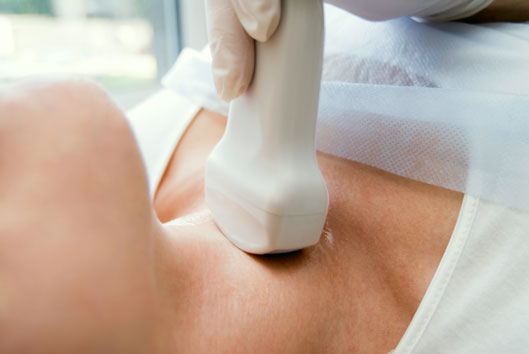
In the thyroid tissue may occur an enlargement, a small tumor that is called nodule. The nodules are actually solid compact tissue masses or tissue masses full of liquid. Most of the nodules of the thyroid gland are benign. In a very small percentage they are responsible for thyroid cancer. However, since some nodules may hide a malignancy, their regular monitoring and examination is quite important. If the nodule is small it can be difficultly detected, while if it is large, it can also appear as a bulge.
In some cases, it may also exercise pressure to the esophagus and cause dyspnea, even difficulty in swallowing. It must be remarked that the nodules of the thyroid are a common finding in almost half of the world population and can be malignant only at a percentage of 5%. Most of the nodules are accidentally detected during the clinical examination, as they have a very small size, only of a few millimeters. The small nodules are difficultly detected, even with the use of ultrasounds.